How A Generator Works
- By BISON
Table of Contents
When there is no access to the main power grid or during crises, generators are essential for supplying backup power. These dependable devices are frequently utilized in residences, workplaces, and enterprises to guarantee a constant supply of electricity. But have you ever pondered the mechanism of a generator? This article will examine a generator’s internal operations and explain how it functions.
What is a Generator?
A generator, often known as an electric generator, is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It is composed of multiple components that operate in concert to produce electricity. When the primary power supply is down or unavailable, generators are made to offer temporary or portable electricity.
Various Generator Types
Inverter generators and conventional generators are the two main categories of generators.
Standard Generators
A conventional generator is the most popular type. They consist of an engine, an alternator, a voltage regulator, and a fuel system. Gasoline, diesel, LPG, or natural gas are just a few of the fuels that may be used to power these generators.
Inverter Generators
Inverter generators are a more advanced and efficient type of generator. They utilize electronic circuitry to convert the generated power into a cleaner and more stable form. Inverter generators are known for their quiet operation and fuel efficiency, making them ideal for camping, outdoor events, and sensitive electronic devices.
8 Basic Components of a Generator
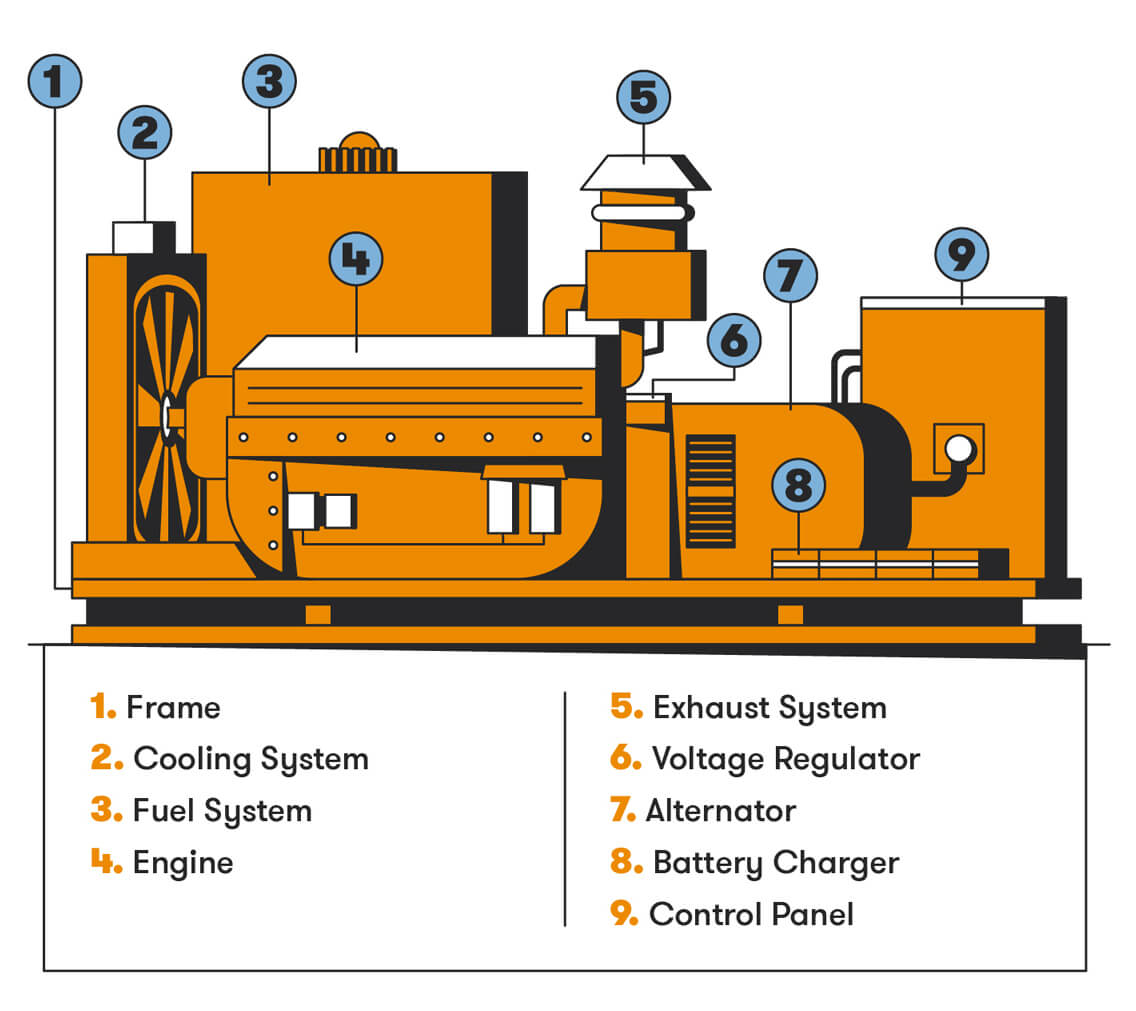
Modern electric generators can vary in size and application, but their inner workings are generally the same across the board. The basic components of an electric generator include:
- Frame: The frame contains and supports the generator’s components. It allows humans to safely handle the generator and protects it from damage.
- Engine: The beating heart of the generator is its engine, which converts fuel into mechanical energy. Gasoline, diesel, propane, or natural gas can all be used to power different types of generators.
- Alternator: The alternator is responsible for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Alternating current (AC) is produced by the combination of a rotor and a stator.
- Fuel System: The task of providing the engine with gasoline falls on the fuel system. Fuel lines, a fuel pump, and a fuel tank are all part of it. The specs of the generator determine the fuel type to be utilized.
- Exhaust System: Diesel and gasoline engines emit exhaust containing toxic chemicals. The exhaust system safely manages and disposes of these gases through a pipe made of iron or steel.
- Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator ensures that the generator produces a consistent and stable voltage output. It regulates the electrical output to prevent damage to connected devices or appliances.
- Battery Charger: Generators rely on a battery to start up. The battery charger is responsible for keeping the battery charged by providing a float voltage of exactly 2.33 volts per cell.
- Control Panel: The control panel is located on the outside of the generator and contains multiple gauges and switches. Features can vary by generator, but the control panel typically includes a starter, engine control gauges and a frequency switch.
How Does a Generator Work?
Step 1: Fuel Provision
Step 2: Start the engine
Step 3: Mechanical Power
Step 4: Electrical Power
What Is an Electric Generator Used For?
Generators have a wide range of applications, including:
- Providing backup power during power outages
- Powering construction sites and outdoor events
- Supporting critical systems in hospitals and data centers
- Enabling remote and off-grid living
Most Popular Posts
QUESTIONS?
CONTACT US TODAY.
buy?
Related Posts

diesel generator components
BISON will explore the key components of diesel generators and understand how each part contributes to their overall performance and reliability.

Common reasons why your generator leaks gasoline
In this guide, BISON covers common causes of gasoline leaks, warning signs to watch for, and how to fix the issue.

portable or standby generators: which one fits your needs?
This article by BISON breaks down the differences between portable and standby generators. By the end, you’ll find which one fits your needs best.
.png)
-qbpqbzxxvtguiuwezisu6wo6j1i29b4m1el1ir1u8o.png)

